Objectives
- Routing in Fortinet FortiGate
- Configuration Steps of Static Routing
- Configuration Steps of Dynamic Routing (BGP)
- Policy Base Routing
- Routing Monitor GUI
- Troubleshooting Commands for Routing in FortiGate
Routing in Fortinet FortiGate Firewall
Routing means how a packet can be sent from a source to destination in a Network.
To perform routing every firewall has a routing table. A routing table contains series of rules which specify the next-hop and active routing sessions. Each routing hop in routing path requires a routing table lookup to pass the packet along as it reaches the destination.
Firewall first find the routing rule in routing table that matches based on the destination address in packet, when performing this match FortiGate evaluate the entire routing table and select most specific route before forwarding the packet to next hop.
What is route lookup?
When a packet arrives on a Firewall interface, Firewall inspects the IPv4 header, detects the destination IPv4 address, and proceeds through the route lookup process.
For each session FortiGate performs route lookup twice.
First lookup performs for the first packet sent by initiator and then for the first reply packet coming from responder. After completing these two lookups firewall updates routing information in session table.
Sequence of packets are routed according to the session table. After a routing table change, route information is flushed from the sessions and must be re-learned.
Static Route
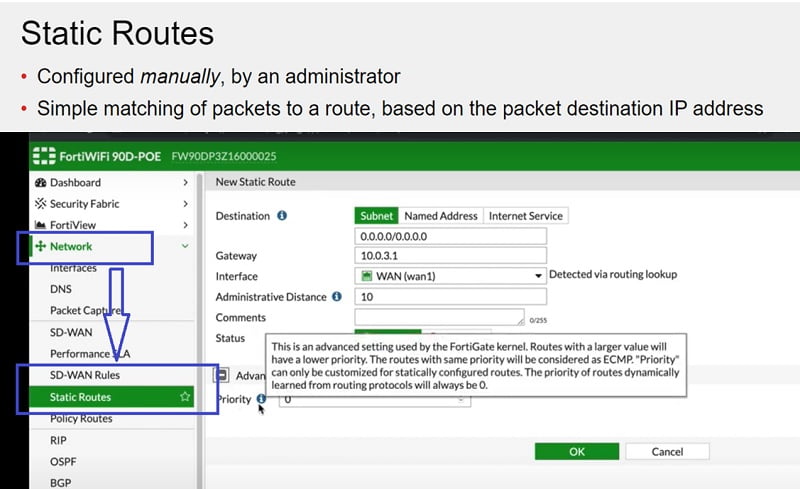
Static Route: Manually configured route, when you are configuring static route, you are telling Firewall to see the packet for specific destination range and specific interface. Example shown in this slide is default static route which means all subnet (0.0.0.0/0) traffic will go via port 1 by using gateway 10.0.3.1 if no matches found in the routing table.
Static Route Configuration in FortiGate:
- GUI-> Network-> Static Routes
- Add New Static Route
- Destination->0.0.0/0
- Gateway-> Firewall Gateway (10.0.3.1)
- AD-> 10(value for static route)
Dynamic Route
For large Network manually configuring routes may not be a practical. Therefore, dynamic routing has been introduced in firewall to learn the route automatically.
Dynamic Routing Protocols supports by FortiGate Firewall
- RIP
- OSPF
- BGP
- IS-IS
In dynamic routing, FortiGate communicates with nearby routers to discover their paths and to advertise its zones to directly connected subnets. Discovered paths are automatically added to the routing table, so verify that neighbour routers are trusted and secure.
Refer below images to configure BGP in FortiGate Firewall.
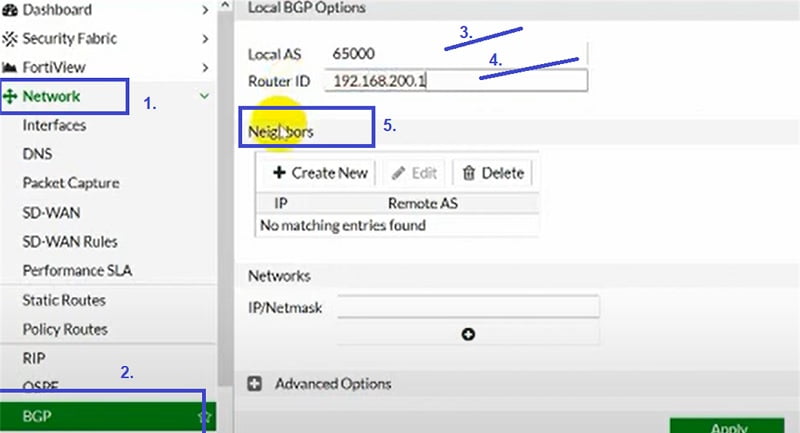
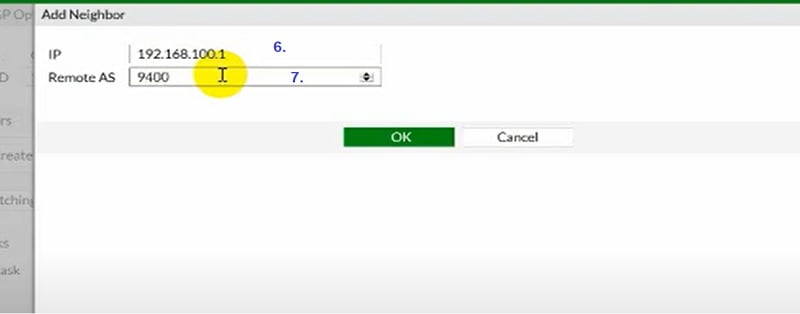
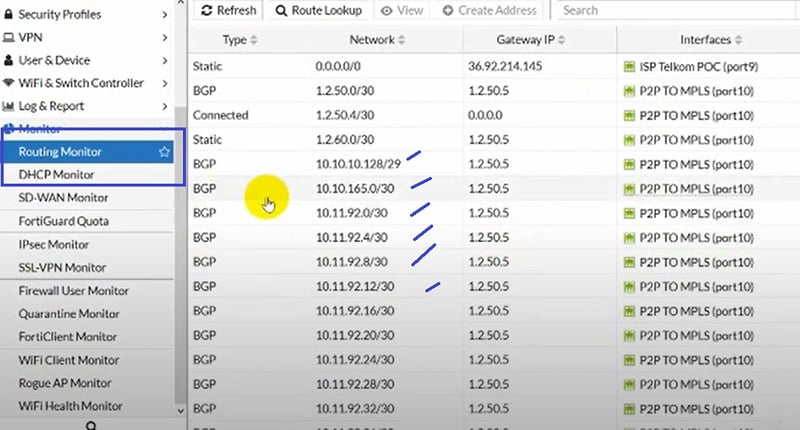
You can verify the routes in Routing Monitor
Policy Based Routing
Policy based routes can match more than only destination IP address. For example if you have 2 ISP links 10 Gpbs and 5 Gbps , one is for higher management for fast internet access and another one for users for average internet reachability.
Policy Based routing has feature to forward traffic on the basis of policy criteria defined in the firewall. If packet matched the policy, firewall bypasses the any routing table. Policy Based route has maintained separate routing table apart for normal firewall routing table.
Moreover, in Policy Based routing Firewall performs
- Traffic is being forwarded by using specified egress interface to the specified gateways
- Uses the routing table instead and Stops policy routing
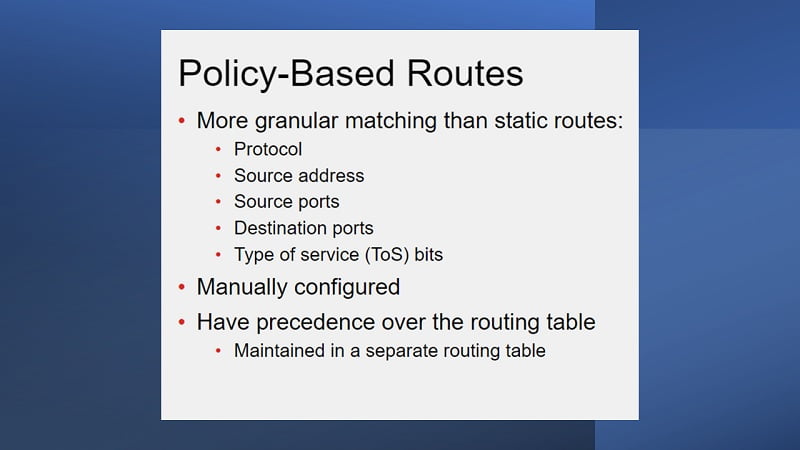
Routing Table Monitor
Routing Table Monitor: In the FortiGate Firewall, GUI shows the active routes. Routing Monitor captures static routes data, directly connected subnets assigned to FortiGate interfaces, connected routes.
If the link is not established or down, route will not be captured by the monitor tab
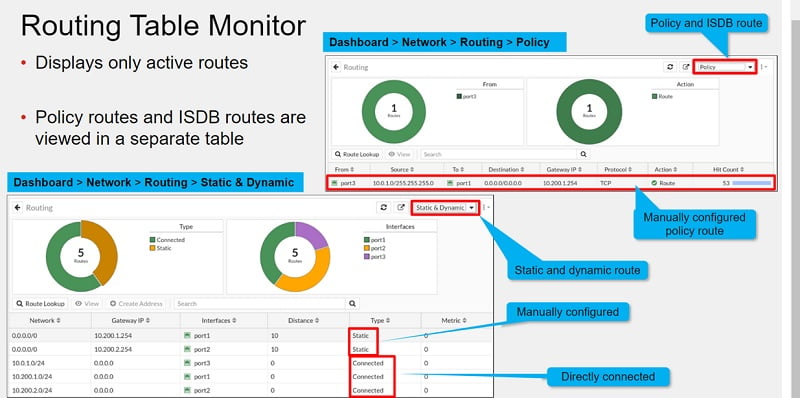
Steps to check Route Lookup in Routing Monitor
Select Route Lookup-> Add search Criteria -> Check Logs
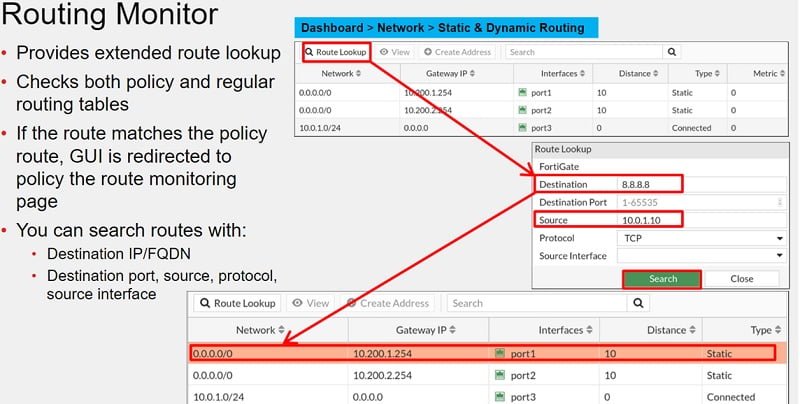
Each of the route listed in routing table includes several attributes with associated values
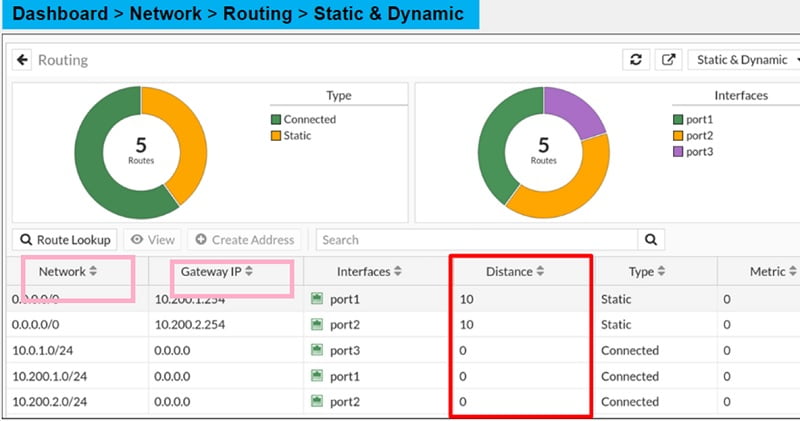
Network Column: list the destination IP address and subnet mask which matched the routing table.
Interface Column: list the interface that will be used to deliver the packet
Distance Column: or administrative distance is used to rank routes from most preferred to least preferred. If multiple routes to the same destination, then smaller distance will be considered for packet transfer.
Distance value 0: Directly Connected
Distance Value 5: DHCP Gateway
Distance Value 10: Static Routes
Distance Value 20: External BGP
Distance Value 110: OSPF Routes
Distance Value 120: RIP Routes
Routing Troubleshoot
CLI Command to check active Routes in FortiGate Firewall:

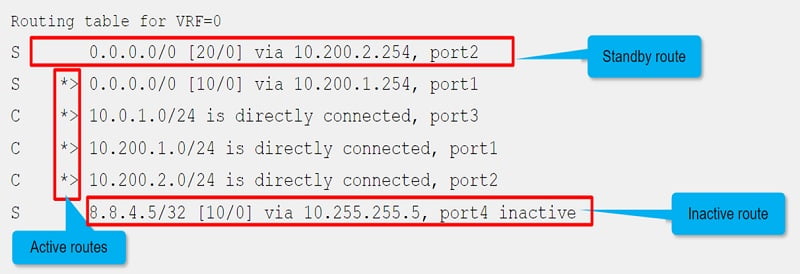
Active, Standby and Inactive Routes

Standby Route
Common Troubleshooting Commands for FortiGate Routing
Some of the commonly used FortiGate CLI commands are:
get router info6 routing-table #show routing table with active routes
get router info routing-table all #all detailed route
get router info6 routing-table database #routing data with active and inactive routes
get router info routing-table database
get router info6 kernel #Forwarding information from Kernel
get router info kernel
diagnose firewall proute6 list #Policy based routing and Load Balancing Info
diagnose firewall proute list
get router <routing-protocol> #Information of enabled routing Protocol
diagnose ip rtcache list #route cache = current sessions w/ routing information
No comments:
Post a Comment