SD-WAN Local Breakout
SD-WAN is a virtual interface which connects different link types using a group of member interfaces. Using SD-WAN simplifies configuration for administrators who can configure a single set of routes and firewall policies and deploy them to all member interfaces. One SD-WAN interface per VDOM is preferable.
SD-WAN is mainly used when multiple WAN links are used and effective WAN usage is achieved using various log balancing methods, such as bandwidth usage, session, or application over routing. Another important feature is link quality measurement, using ping or http echo FortiGate can determine latency, jitter or packet loss percentage for each link and dynamically select links based on these capacities, this guarantees high-availability HA for commercial-critical applications.
SD-WAN Load Balancing Methods
SD-WAN load balancing uses traffic distribution that is like ECMP, however SD-WAN link load balancing includes one more balancing method volume, by default the load balancing mode is set to Source IP based. But this can be changed to any of the following methods based on:
- Source IP: All traffic from the source IP is sent to the same interface
- Weight: Interface with higher weights have higher priority
- Usage: All traffic is sent to first interface on the list, when the bandwidth on that interface exceeds the spillover limit new traffic is sent to next interface
- Source Destination IP: All traffic from Source IP to destination IP is sent to the same
- Measured Volume: Traffic is load balance based on traffic and volume, more traffic is sent to interface with higher volume ratios
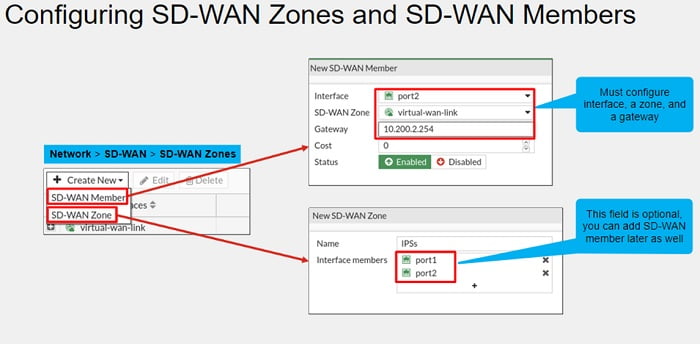
FortiGate SD-WAN Zones
You can divide SD-WAN interface into smaller or larger groups called SD-WAN zones, you can use these SD-WAN zones in firewall policies to allow you to have more granular control over traffic being inspected and allowed.
Multiple SD-WAN zones can be created for SD-WAN members, by default, FortiGate Firewall has the virtual WAN link zone created.
However, SD-WAN members cannot be shared between multiple zones.
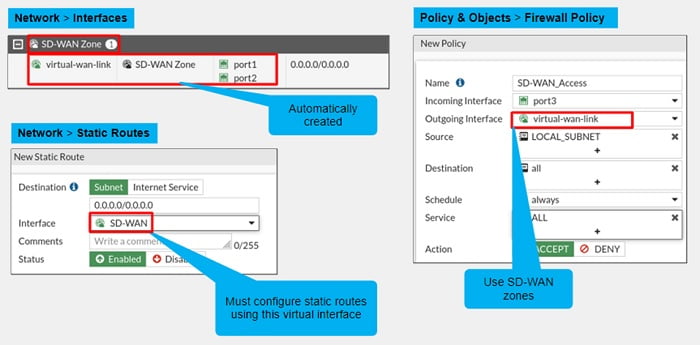
Creating Routes and Firewall Policies
After you enable SD-WAN and configure member interfaces in load balancing methods, a logical interface with name SD-WAN is automatically added to the interface list when you create a static route. Routes in the FortiGate Firewall through SD-WAN must be created by using this virtual interface. For configuring firewall policies, you must use SD-WAN zones as source interface or destination interface.
You must configure the default route while implementing SD-WAN, the default route configuration using SD-WAN interface doesn’t require a gateway address because FortiGate forwards packets to appropriate gateways based on member interface gateway information.
Performance SLA
Generally, three parts make up the performance SLA window: the link health monitor, SLA targets and status check.
1. Link Health Monitor:
It’s a mechanism which detects where the router on the path is stopped or degraded, FortiGate can check health and status of each SD-WAN member interface participating in a performance SLA, based on the detection mode you have selected.
- Active: Link health is measured by sending pro packets to the configured server.
- Passive: Link health is measured using session information that is captured on firewall policies that have passive health WAN measurement enabled.
- Prefer Passive: Link health is measured using traffic passing through SD-WAN members
GUI provide three protocol options through which to perform the status check Ping, HTTP and DNS but on CLI you have six options those are Ping, HTTP, DNS, TCP-echo, UDP-echo and TWAMP (Two-Way Active Management Protocol).
2. SLA Targets:
The quality of service for the traffic associated with this performance SLA is defined by the SLA target. An SD-WAN member assigned to this performance SLA must meet the SLA target to get selected over the other participating links. You can configure latency, Jitter and packet loss thresholds to meet your needs and create granular SLA targets to fine tune SD-WAN for specific applications.
3. Link Status:
The link status contains settings which specifies, how often a system checks the link status to determine if it needs to transfer traffic to another link. The failure before an active and restore link after setting prevents the system continuously sending traffic back and forth between links, the condition known as flapping.
Link Quality Measurement
The performance SLA or health checks measures the quality of links connected to the member interface participating in a performance SLA. Three different criteria are used for these measurements – latency, Jitter and Packet loss percentage.
SD-WAN Rules Internet Services and Applications
SD-WAN can use internet services databases as well as the application control database to steer applications along a specific link, FortiGuard maintains these databases and FortiGate periodically gets an updated copy. SSL inspection should be enabled for identifying applications accurately. SD-WAN can use ISDB and application control to route application-specific traffic.
FortiGate SD-WAN Rules
FortiGate SD-WAN offers four strategies for selecting outgoing interfaces: Manual, Best-Quality, Lowest Cost and Maximize Bandwidth (SLA).
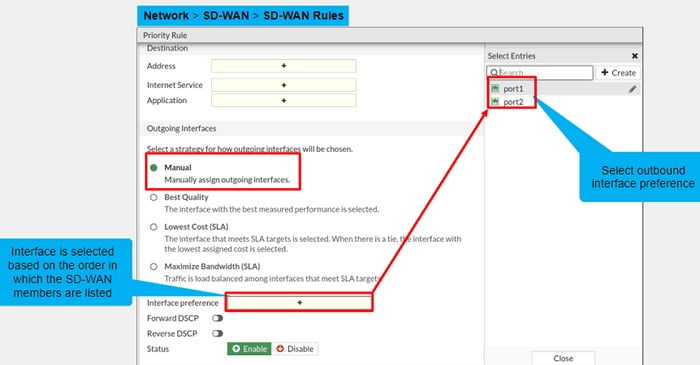
- Manual: You can specify the interface priority you want to send traffic out from if the traffic matches the rule criteria the traffic will go out from the first available interface based on the interface preference.
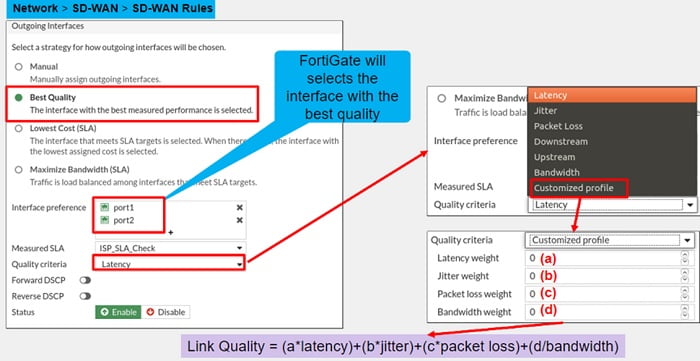
- Best-Quality: This best-quality strategy is based on performance of the network. By default, the quality criteria are 10 percent, but you can change it. The quality check on the performance SLA is using only the server information and health check against the quality criteria. You can use options of Latency, Jitter and Packet loss percentage. You can also use the bandwidth options downstream-bandwidth, upstream-bandwidth, or bi-directional bandwidth, so that FortiGate selects the link based on available bandwidth of incoming, outgoing, or bi-directional traffic. The last option, custom profile one allows database link selection on the combination of its criteria values, the link quality is determined by the equation, the larger the value the more weight that criteria will have in the selection, leave that weight value at zero to exclude those criteria from the equation.
- Lowest Cost: When you use the lowest cost SLA strategy you select a SLA target from the performance SLA that you want to measure the traffic against, even if the performance SLA has multiple SLA targets you can select only one of the SLA targets from that particular performance SLA.
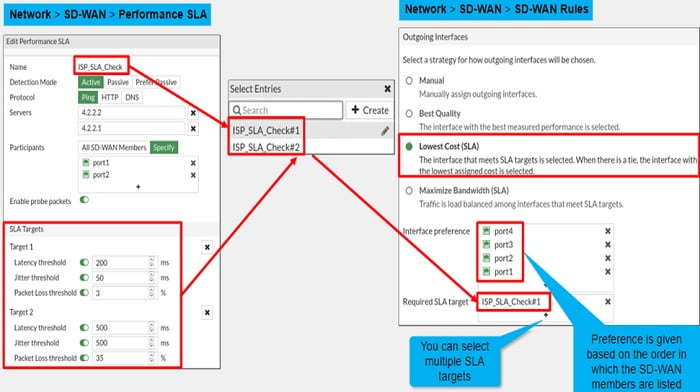
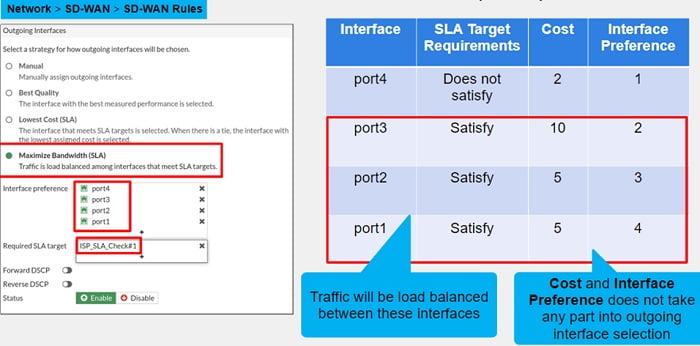
- Maximize Bandwidth (SLA) : This feature introduces a new load balance mode for SD-WAN rule. If traffic matches the rule specification, traffic is load balanced amongst the selected members that satisfies the SLA specification. Using this method FortiGate doesn’t take cost or priority into consideration.
FortiGate SD-WAN Diagnostics
FortiGate SD-WAN diagnostics components include monitoring SD-WAN Link Usage, SD-WAN Link Quality Status and SD-WAN Traffic Routing.
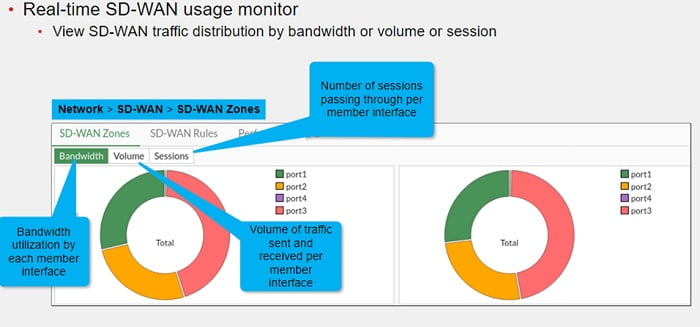
1. SD-WAN Link Usage: You can use this to view traffic distribution between the member interface based on Bandwidth, Volume and Sessions.
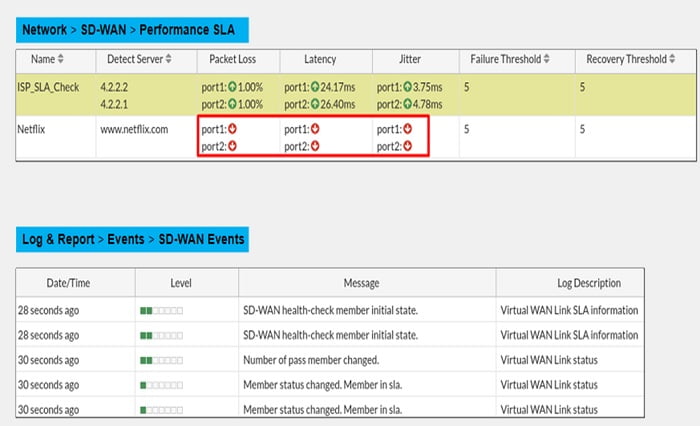
2. SD-WAN Link Quality Status: Monitoring link quality status of SD-WAN member interfaces, you can investigate any prolonged issues with packet loss and latency to ensure your network traffic doesn’t experience outage or degraded performance.
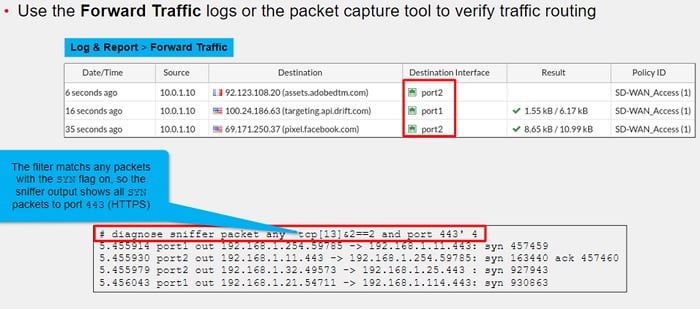
3. SD-WAN Traffic Routing: You can use the destination interface column in the forward traffic logs to verify traffic is egressing the SD-WAN member interfaces.
No comments:
Post a Comment