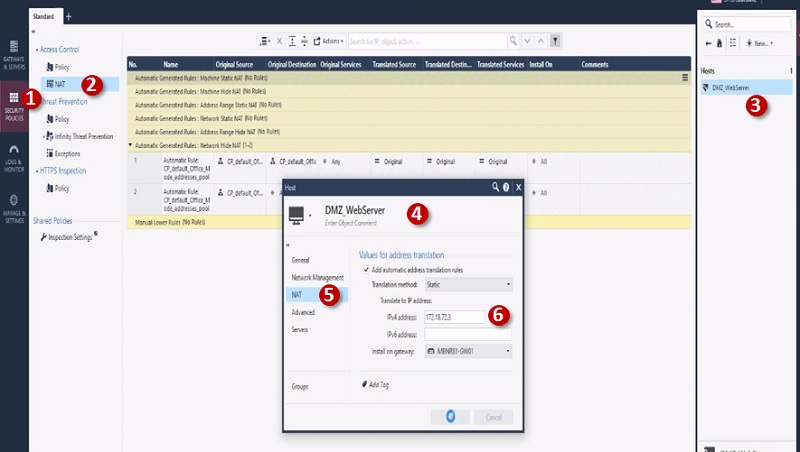
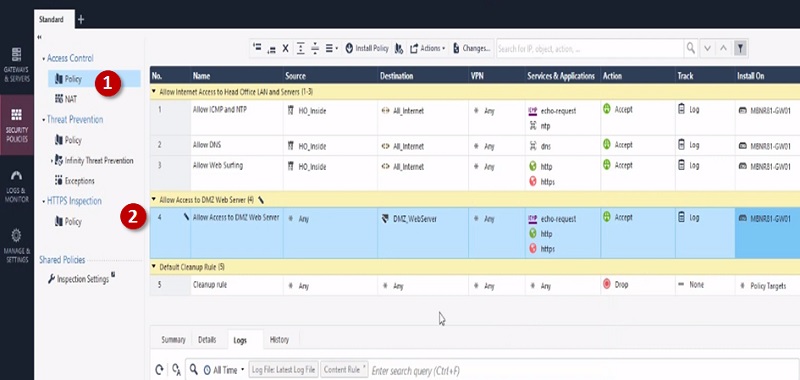
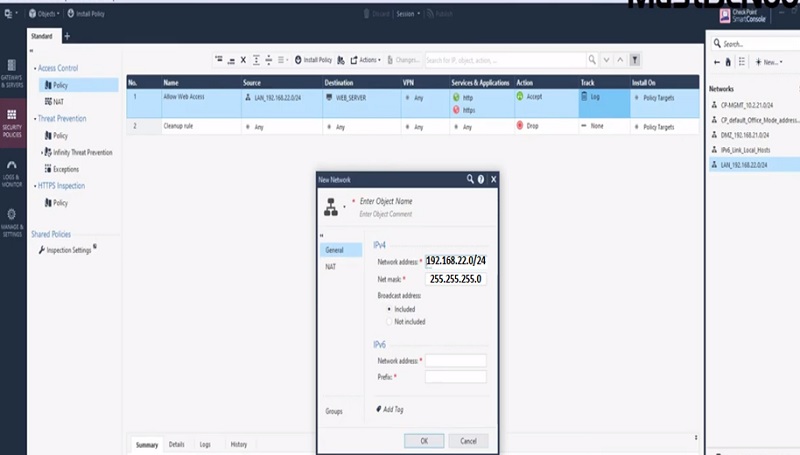
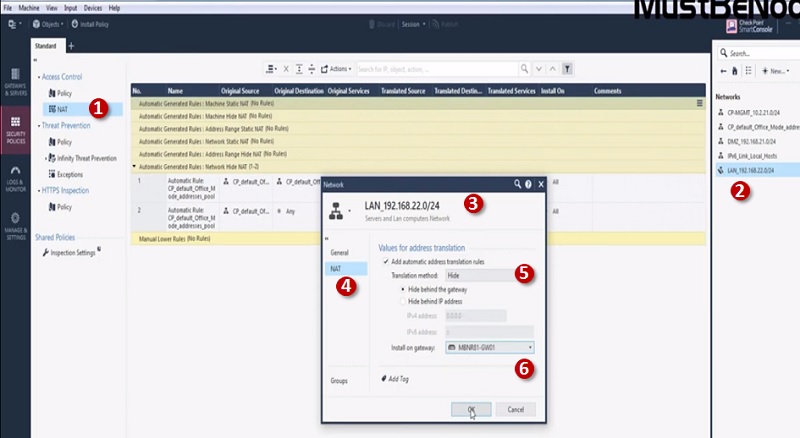
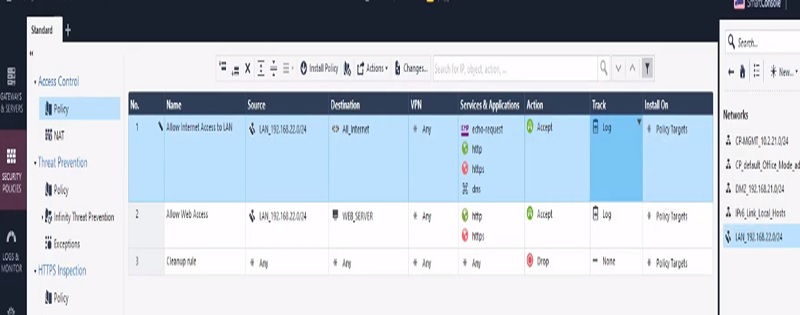
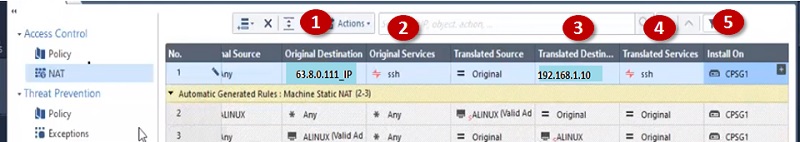
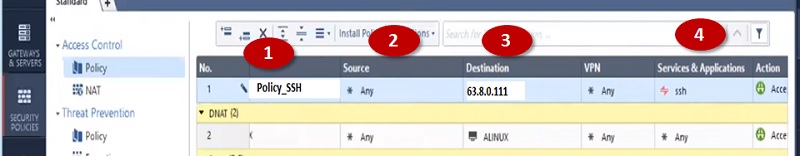
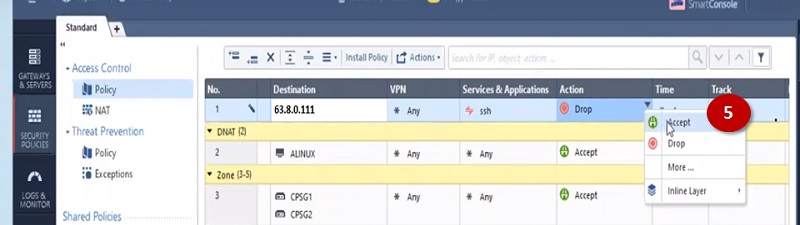
Before starting to explore Checkpoint NGX Firewall technologies, it is critical to comprehend Checkpoint 3-Tier architecture. This architecture describes the relationships between the components of Checkpoint, as well as how they work together as a harmonious unit. Each element has its own specific responsibilities.
Checkpoint 3-Tier Architecture
Checkpoint is a Next Generation Firewall which has three basic pillars
- Security Management Server
- Security Gateway (Enforcement Module)
- SmartConsole
Let’s understand, how these components work together as a harmonious unit:
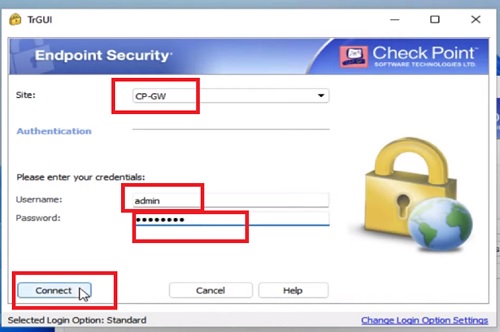
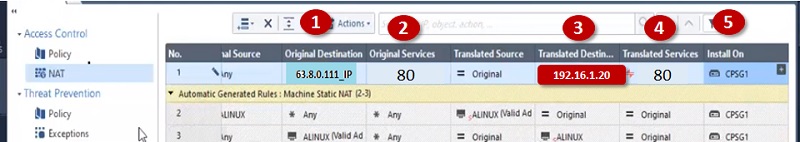
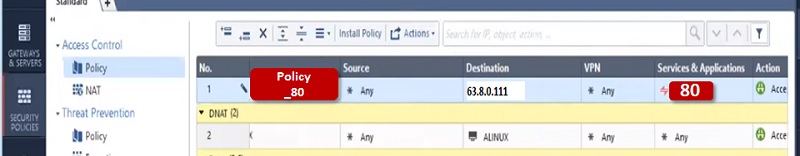
- Security Admin access SmartConsole and initiate communication with Security Management Gateway.
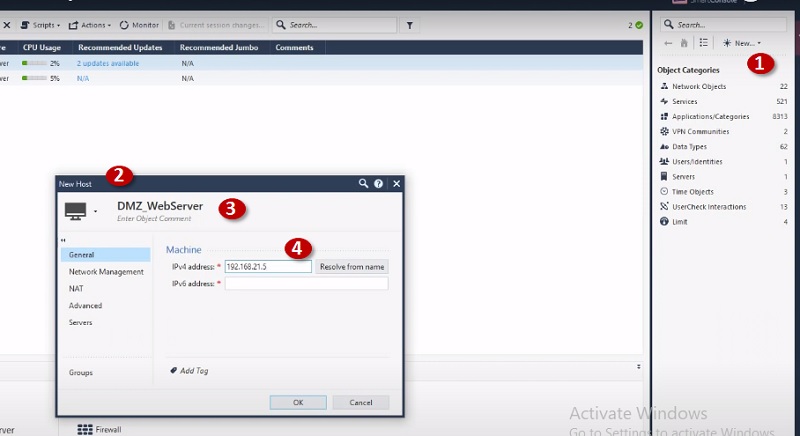
- Security Admin makes the changes in firewall policy and install policy.
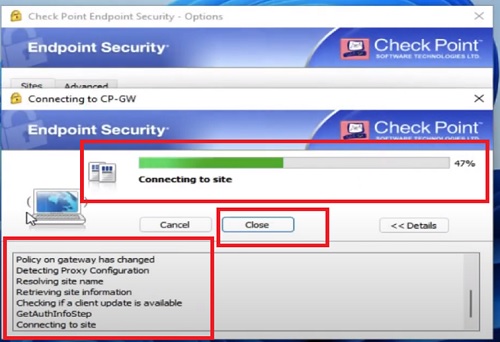
- Security Management Server validate and verify the changes and confirms if change is error free and forward change policy package to Security Gateway
- Security Gateway fetch the changes and apply it to firewall packet flow which is passing through the gateway.
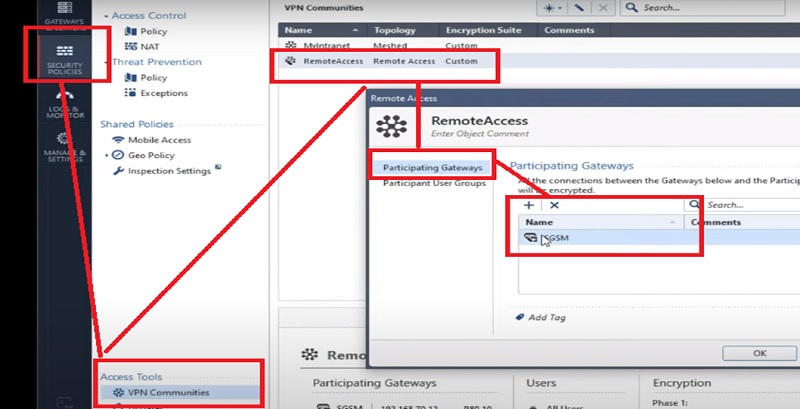
Security Management Server (SMS)
As its name implies, Security Management Server is a server component. As being a server component its work is to store firewall policies, repository of policies, rules, NAT policies, VPN configuration, user-database, user-groups, user permissions, authentications, storage of certificates.
SMS distributes policies and rules to multiple or single gateway. Single Smart Center Server can manage multiple gateways.
SMS can act like a log server which means it can store logs, those are generated by firewall.
Installation Platform -> SMS can be deployed on below platforms.
Key job performs by Security Management Gateway
- Store policies, act as a database
- Store log and log files
- Maintain and store Firewall database
- Deployed on Linux, Windows, and Gaia OS
- Single Security Management Gateway can manage multiple Gateways.
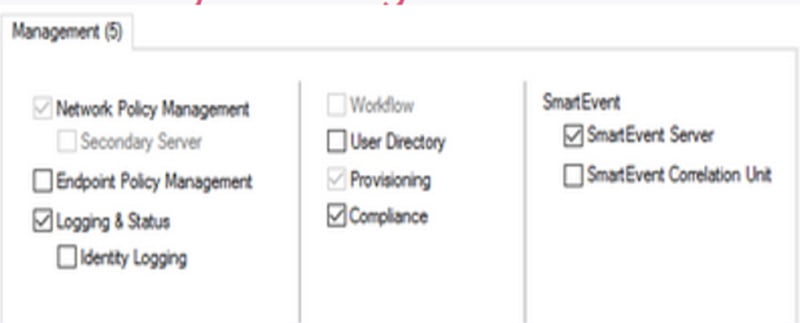
Management Gateway has below featured blades
- Network Policy Management — Security Gateway policies are created and managed by Network Policy Management
- Endpoint Policy Management — Endpoint Policies are created and managed by it
- Logging & Status – Logs are managed by Logging and Status
- Workflow — Audit and approval of management policy
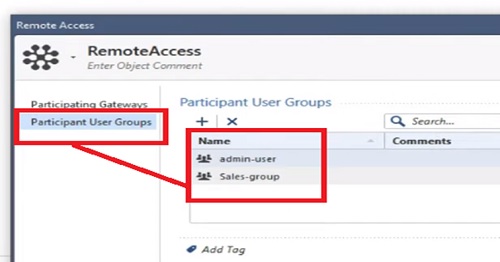
- User Directory — Authentication and user database manages by it
- Provisioning — Maintenance tool
- Compliance — Audit and apply compliance as per rules and regulations
- SmartEvent — Logs and Events management
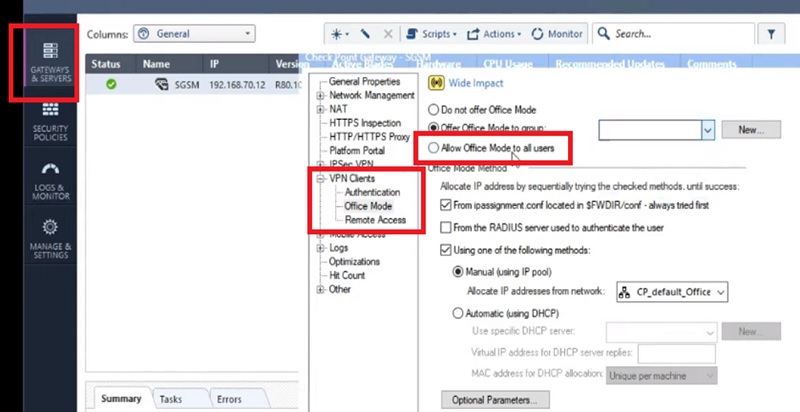
Security Gateway
Security Gateway is also known as Enforcement Module. You will see it very commonly when people call it an Enforcement Module.
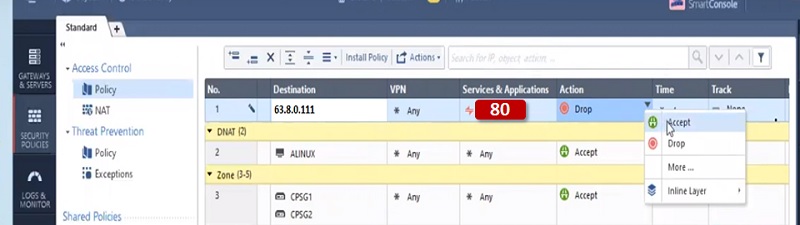
Its work is to regulate the policy, Security Gateway receives policies from Smart Center Server and applies policies in order of top-to-bottom against every packet that the firewall receives in inbound/outbound direction.
Once a rule is defined in the firewall, the gateway acts as a decision maker which can protect the traffic as per defined rule.
Key Jobs perform by Security Gateway
- All inbound and outbound traffic of Next Generation firewalls are inspected on Gateway.
- Gateway verifies the packet and compares it with security policy and then applies security policy accordingly.
- Network defence is done by Security Gateway.
- Gateway protects the traffic by applying 3-way handshake OR stateful inspection.
- Installation can be done -> Linux, Windows, and Gaia OS
Below is the list of Security Blades which are available in Security Gateway. Security Blades are the feature of the firewall. For example, URL filtering, IPS, Anti-virus etc.

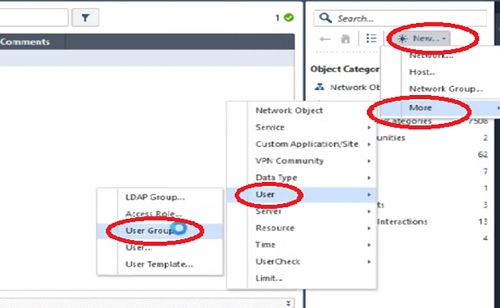
Smart Console
To manage Smart Center Server, the admin needs GUI to access the application or features. Smart Console is the platform which is used to access the features of Next Generation Firewall.
Smart Console can only be accessible from Windows, it does not support Gaia OS.
First policies are configured by using SmartDashboard and further saved in the Smart Management Server.
Below packages are downloaded as a SmartConsole package:
- Smart Dashboard
- Smart View Tracker
- Smart View Monitor
- Smart Update
- Smart Log
- Smart Event
- Smart Provisioning
- Smart Reporter
- Smart Endpoint
- Smart Domain Manager
- Smart Event Intro
- Secure Client Packaging Tool
Deployment Option
Based on Checkpoint product we can choose deployment options
- Check Point Security Appliance. Hardware and software options are required to run Check Point Network Security System.
- Open Server. Gaia OS can be installed on any of the compatible server
- A Virtual Machine. Gaia can be configured on virtual machines, cloud-based platforms like VMware, cloud platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba, and Oracle.
Another method to deploy the device in network
- Standalone -> Single device in which Security Gateway and SMS are installed on same machine.
- Distributed -> Console and Security Gateway are using different machines or server.
Distributed Deployment is the commonly used approach in the network.
You may further need to explore SmartConsole deployment, Smart Management Server features and deployment and Security Gateway components. These topics will help you to understand the Checkpoint 3-Tier architecture.